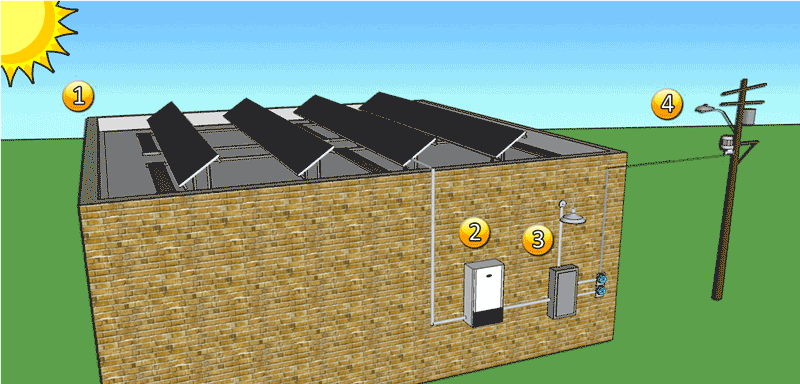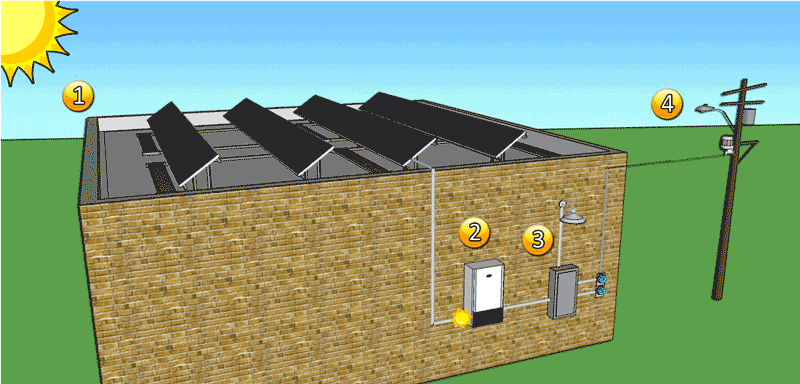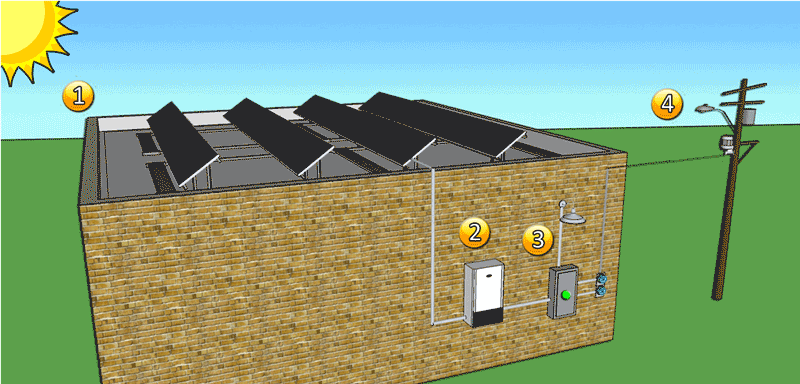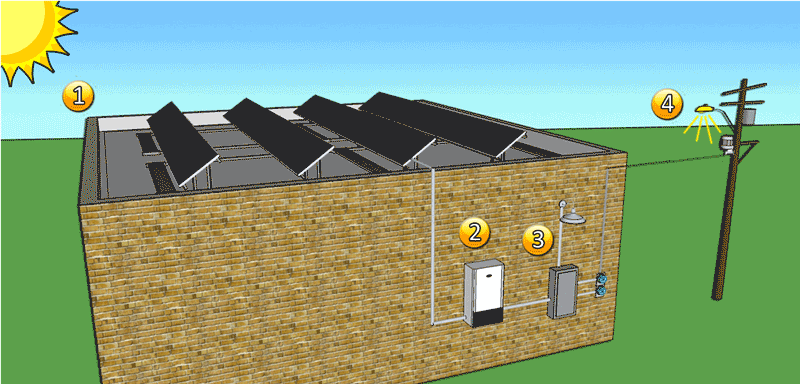
Forms-
The total energy of a system can be subdivided and classified in various ways. For example, Classical mechanics distinguishes between kinetic energy, which is determined by an object's movement through space, and potential energy, which is a function of the position of an object within a field. It may also be convenient to distinguish gravitational energy, electric energy, thermal energy, several types of nuclear energy (which utilize potentials from the nuclear force and the weak force), electric energy (from the electric field), and magnetic energy (from the magnetic field), among others. Many of these classifications overlap; for instance, thermal energy usually consists partly of kinetic and partly of potential energy. Some types of energy are a varying mix of both potential and kinetic energy. An example is mechanical energy which is the sum of (usually macroscopic) kinetic and potential energy in a system. Elastic energy in materials is also dependent upon electrical potential energy (among atoms and molecules), as is chemical energy, which is stored and released from a reservoir of electrical potential energy between electrons, and the molecules or atomic nuclei that attract them..The list is also not necessarily complete. Whenever physical scientists discover that a certain phenomenon appears to violate the law of energy conservation, new forms are typically added that account for the discrepancy.
Heat and work are special cases in that they are not properties of systems, but are instead properties of processes that transfer energy. In general we cannot measure how much heat or work are present in an object, but rather only how much energy is transferred among objects in certain ways during the occurrence of a given process. Heat and work are measured as positive or negative depending on which side of the transfer we view them from.
Potential energies are often measured as positive or negative depending on whether they are greater or less than the energy of a specified base state or configuration such as two interacting bodies being infinitely far apart. Wave energies (such as radiant or sound energy), kinetic energy, and rest energy are each greater than or equal to zero because they are measured in comparison to a base state of zero energy: "no wave", "no motion", and "no inertia", respectively.

Measurement & Unit-
Energy, like mass, is a scalar physical quantity. The joule is the International System of Units (SI) unit of measurement for energy. It is a derived unit of energy, work, or amount of heat. It is equal to the energy expended (or work done) in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre. However energy is also expressed in many other units such as ergs, calories, British Thermal Units, kilowatt-hours and kilocalories for instance. There is always a conversion factor for these to the SI unit; for instance; one kWh is equivalent to 3.6 million joules.
The SI unit of power (energy per unit time) is the watt, which is simply a joule per second. Thus, a joule is a watt-second, so 3600 joules equal a watt-hour. The CGS energy unit is the erg, and the imperial and US customary unit is the foot pound. Other energy units such as the electron volt, food calorie or thermodynamic kcal (based on the temperature change of water in a heating process), and BTU are used in specific areas of science and commerce and have unit conversion factors relating them to the joule.
Because energy is defined as the ability to do work on objects, there is no absolute measure of energy. Only the transition of a system from one state into another can be defined and thus energy is measured in relative terms. The choice of a baseline or zero point is often arbitrary and can be made in whatever way is most convenient for a problem. For example in the case of measuring the energy deposited by X-rays as shown in the accompanying diagram, conventionally the technique most often employed is calorimetry. This is a thermodynamic technique that relies on the measurement of temperature using a thermometer or of intensity of radiation using a bolometer.
Energy density is a term used for the amount of useful energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. For fuels, the energy per unit volume is sometimes a useful parameter. In a few applications, comparing, for example, the effectiveness of hydrogen fuel to gasoline it turns out that hydrogen has a higher specific energy than does gasoline, but, even in liquid form, a much lower energy density.

Transformation-
Energy may be transformed between different forms at various efficiencies. Items that transform between these forms are called transducers. Examples of transducers include a battery, from chemical energy to electric energy; a dam: gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy of moving water (and the blades of a turbine) and ultimately to electric energy through an electric generator.
There are strict limits to how efficiently energy can be converted into other forms of energy via work, and heat as described by Carnot's theorem and the second law of thermodynamics. These limits are especially evident when an engine is used to perform work. However, some energy transformations can be quite efficient. The direction of transformations in energy (what kind of energy is transformed to what other kind) is often determined by entropy (equal energy spread among all available degrees of freedom) considerations. In practice all energy transformations are permitted on a small scale, but certain larger transformations are not permitted because it is statistically unlikely that energy or matter will randomly move into more concentrated forms or smaller spaces.
Energy transformations in the universe over time are characterized by various kinds of potential energy that has been available since the Big Bang, later being "released" (transformed to more active types of energy such as kinetic or radiant energy), when a triggering mechanism is available. Familiar examples of such processes include nuclear decay, in which energy is released that was originally "stored" in heavy isotopes (such as uranium and thorium), by nucleosynthesis, a process ultimately using the gravitational potential energy released from the gravitational collapse of supernovae, to store energy in the creation of these heavy elements before they were incorporated into the solar system and the Earth. This energy is triggered and released in nuclear fission bombs or in civil nuclear power generation. Similarly, in the case of achemical explosion, chemical potential energy is transformed to kinetic energy and thermal energy in a very short time. Yet another example is that of a pendulum. At its highest points the kinetic energy is zero and the gravitational potential energyis at maximum. At its lowest point the kinetic energy is at maximum and is equal to the decrease of potential energy. If one (unrealistically) assumes that there is no friction or other losses, the conversion of energy between these processes would be perfect, and the pendulum would continue swinging forever.


Conservation-
According to conservation of energy, energy can neither be created (produced) nor destroyed by itself. It can only be transformed. The total inflow of energy into a system must equal the total outflow of energy from the system, plus the change in the energy contained within the system. Energy is subject to a strict global conservation law; that is, whenever one measures (or calculates) the total energy of a system of particles whose interactions do not depend explicitly on time, it is found that the total energy of the system always remains constant.
Most kinds of energy (with gravitational energy being a notable exception) are subject to strict local conservationlaws as well. In this case, energy can only be exchanged between adjacent regions of space, and all observers agree as to the volumetric density of energy in any given space. There is also a global law of conservation of energy, stating that the total energy of the universe cannot change; this is a corollary of the local law, but not vice versa.
This law is a fundamental principle of physics. As shown rigorously by Noether's theorem, the conservation of energy is a mathematical consequence of translational symmetry of time, a property of most phenomena below the cosmic scale that makes them independent of their locations on the time coordinate. Put differently, yesterday, today, and tomorrow are physically indistinguishable. This is because energy is the quantity which is canonical conjugate to time. This mathematical entanglement of energy and time also results in the uncertainty principle - it is impossible to define the exact amount of energy during any definite time interval. The uncertainty principle should not be confused with energy conservation - rather it provides mathematical limits to which energy can in principle be defined and measured.
Each of the basic forces of nature is associated with a different type of potential energy, and all types of potential energy (like all other types of energy) appears as system mass, whenever present. For example, a compressed spring will be slightly more massive than before it was compressed. Likewise, whenever energy is transferred between systems by any mechanism, an associated mass is transferred with it.
Conservation of energy and mass in transformation-
Energy gives rise to weight when it is trapped in a system with zero momentum, where it can be weighed. It is also equivalent to mass, and this mass is always associated with it. Mass is also equivalent to a certain amount of energy, and likewise always appears associated with it, as described in mass-energy equivalence. The formula E = mc², derived by Albert Einstein (1905) quantifies the relationship between rest-mass and rest-energy within the concept of special relativity. In different theoretical frameworks, similar formulas were derived by J. J. Thomson (1881), Henri Poincaré (1900), Friedrich Hasenöhrl (1904) and others.
Matter may be converted to energy (and vice versa), but mass cannot ever be destroyed; rather, mass/energy equivalence remains a constant for both the matter and the energy, during any process when they are converted into each other. However, since is extremely large relative to ordinary human scales, the conversion of ordinary amount of matter (for example, 1 kg) to other forms of energy (such as heat, light, and other radiation) can liberate tremendous amounts of energy (~ joules = 21 megatons of TNT), as can be seen in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Conversely, the mass equivalent of a unit of energy is minuscule, which is why a loss of energy (loss of mass) from most systems is difficult to measure by weight, unless the energy loss is very large. Examples of energy transformation into matter (i.e., kinetic energy into particles with rest mass) are found in high-energy nuclear physics.
Reversible and non-reversible transformations-
Thermodynamics divides energy transformation into two kinds: reversible processes and irreversible processes. An irreversible process is one in which energy is dissipated (spread) into empty energy states available in a volume, from which it cannot be recovered into more concentrated forms (fewer quantum states), without degradation of even more energy. A reversible process is one in which this sort of dissipation does not happen. For example, conversion of energy from one type of potential field to another, is reversible, as in the pendulum system described above. In processes where heat is generated, quantum states of lower energy, present as possible excitations in fields between atoms, act as a reservoir for part of the energy, from which it cannot be recovered, in order to be converted with 100% efficiency into other forms of energy. In this case, the energy must partly stay as heat, and cannot be completely recovered as usable energy, except at the price of an increase in some other kind of heat-like increase in disorder in quantum states, in the universe (such as an expansion of matter, or a randomisation in a crystal).


Scientific Use-
In classical mechanics, energy is a conceptually and mathematically useful properas it is a conserved quantity. Several formulations of mechanics have been developed using energy as a core concept.
The total energy of a system is sometimes called the Hamiltonian, after William Rowan Hamilton. The classical equations of motion can be written in terms of the Hamiltonian, even for highly complex or abstract systems. These classical equations have remarkably direct analogs in nonrelativistic quantum mechanics.
Another energy-related concept is called the Lagrangian, after Joseph-Louis Lagrange. This is even more fundamental than the Hamiltonian, and can be used to derive the equations of motion. It was invented in the context of classical mechanics, but is generally useful in modern physics. The Lagrangian is defined as the kinetic energy minus the potential energy. Usually, the Lagrange formalism is mathematically more convenient than the Hamiltonian for non-conservative systems (such as systems with friction).
Noether's theorem (1918) states that any differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system has a corresponding conservation law. Noether's theorem has become a fundamental tool of modern theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. A generalisation of the seminal formulations on constants of motion in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics (1788 and 1833, respectively), it does not apply to systems that cannot be modeled with a Lagrangian; for example, dissipative systems with continuous symmetries need not have a corresponding conservation law.
In the context of chemistry, energy is an attribute of a substance as a consequence of its atomic, molecular or aggregate structure. Since a chemical transformation is accompanied by a change in one or more of these kinds of structure, it is invariably accompanied by an increase or decrease of energy of the substances involved. Some energy is transferred between the surroundings and the reactants of the reaction in the form of heat or light; thus the products of a reaction may have more or less energy than the reactants. A reaction is said to be exergonic if the final state is lower on the energy scale than the initial state; in the case of endergonic reactions the situation is the reverse. Chemical reactions are invariably not possible unless the reactants surmount an energy barrier known as the activation energy. The speed of a chemical reaction (at given temperature T) is related to the activation energy E, by the Boltzmann's population factor e−E/kT – that is the probability of molecule to have energy greater than or equal to E at the given temperature T. This exponential dependence of a reaction rate on temperature is known as the Arrhenius equation.The activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction can be in the form of thermal energy.
In biology, energy is an attribute of all biological systems from the biosphere to the smallest living organism. Within an organism it is responsible for growth and development of a biological cell or an organelle of a biological organism. Energy is thus often said to be stored by cells in the structures of molecules of substances such as carbohydrates (including sugars), lipids, and proteins, which release energy when reacted with oxygen in respiration. In human terms, the human equivalent (H-e) (Human energy conversion) indicates, for a given amount of energy expenditure, the relative quantity of energy needed for human metabolism, assuming an average human energy expenditure of 12,500kJ per day and a basal metabolic rate of 80 watts. For example, if our bodies run (on average) at 80 watts, then a light bulb running at 100 watts is running at 1.25 human equivalents (100 ÷ 80) i.e. 1.25 H-e. For a difficult task of only a few seconds' duration, a person can put out thousands of watts, many times the 746 watts in one official horsepower. For tasks lasting a few minutes, a fit human can generate perhaps 1,000 watts. For an activity that must be sustained for an hour, output drops to around 300; for an activity kept up all day, 150 watts is about the maximum. The human equivalent assists understanding of energy flows in physical and biological systems by expressing energy units in human terms: it provides a "feel" for the use of a given amount of energy
Sunlight is also captured by plants as chemical potential energy in photosynthesis, when carbon dioxide and water (two low-energy compounds) are converted into the high-energy compounds carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Plants also release oxygen during photosynthesis, which is utilized by living organisms as an electron acceptor, to release the energy of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Release of the energy stored during photosynthesis as heat or light may be triggered suddenly by a spark, in a forest fire, or it may be made available more slowly for animal or human metabolism, when these molecules are ingested, and catabolism is triggered by enzyme action.